
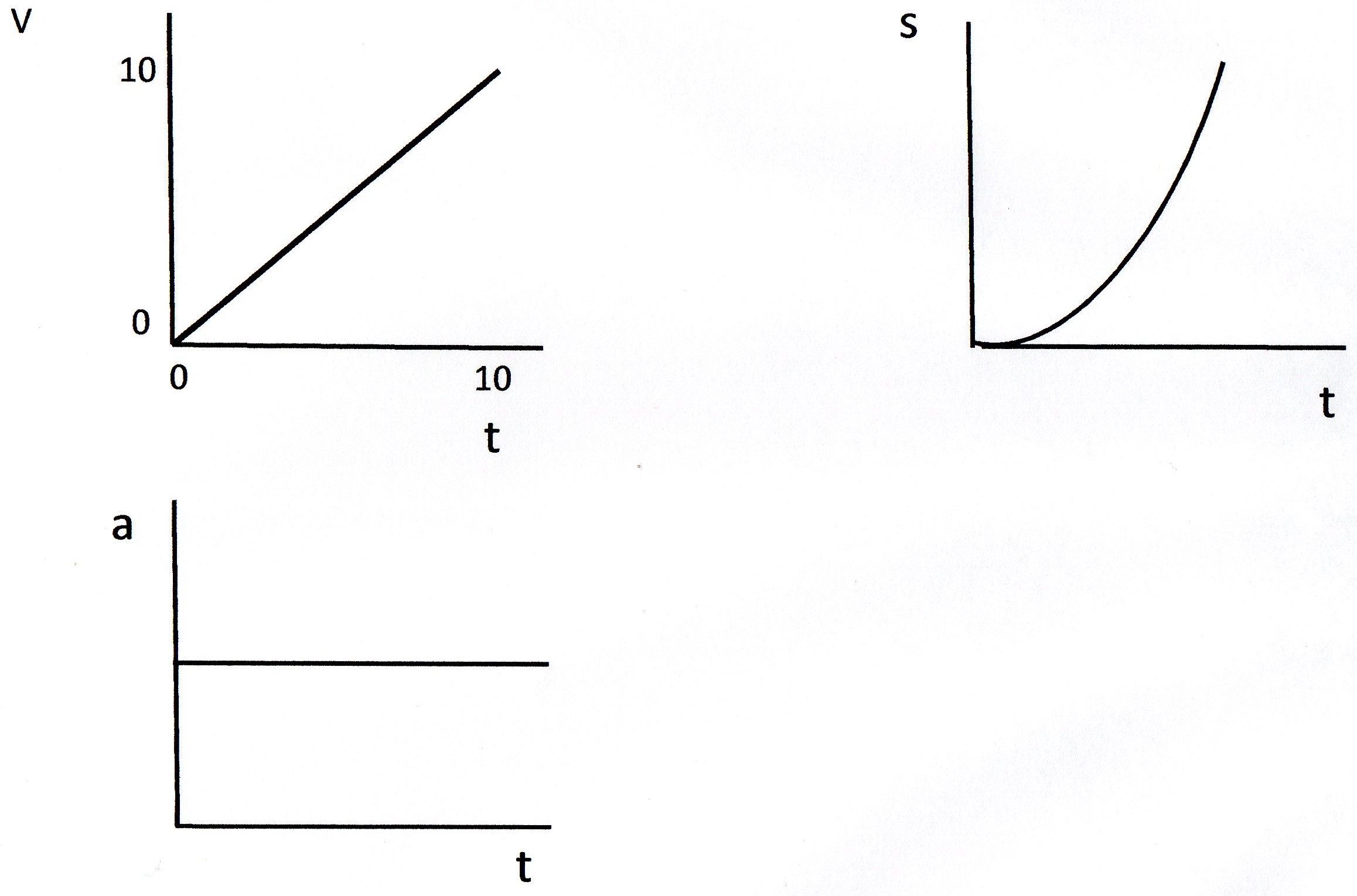
In physics, however, they do not have the same meaning and they are distinct concepts. In everyday language, most people use the terms “speed” and “velocity” interchangeably. However, under many circumstances, we can find precise values for instantaneous velocity without calculus. Mathematically, finding instantaneous velocity, v v, at a precise instant t t can involve taking a limit, a calculus operation beyond the scope of this text. (Police give tickets based on instantaneous velocity, but when calculating how long it will take to get from one place to another on a road trip, you need to use average velocity.) Instantaneous velocity v v is the average velocity at a specific instant in time (or over an infinitesimally small time interval). A car’s speedometer, for example, shows the magnitude (but not the direction) of the instantaneous velocity of the car. Over such an interval, the average velocity becomes the instantaneous velocity or the velocity at a specific instant. When we carry this process to its logical conclusion, we are left with an infinitesimally small interval. The smaller the time intervals considered in a motion, the more detailed the information. Elapsed time Δ t Δ t is the difference between the ending time and beginning time,įigure 2.9 A more detailed record of an airplane passenger heading toward the back of the plane, showing smaller segments of his trip. and end at 11:50 A.M., so that the elapsed time would be 50 min. For example, a lecture may start at 11:00 A.M. To find elapsed time, we note the time at the beginning and end of the motion and subtract the two. How does time relate to motion? We are usually interested in elapsed time for a particular motion, such as how long it takes an airplane passenger to get from his seat to the back of the plane. This allows us to not only measure the amount of time, but also to determine a sequence of events. We could then use the pendulum to measure time by counting its swings or, of course, by connecting the pendulum to a clock mechanism that registers time on a dial.
Distance vs time scatter plot physics drop block full#
We might, for example, observe that a certain pendulum makes one full swing every 0.75 s. The SI unit for time is the second, abbreviated s. The amount of time or change is calibrated by comparison with a standard. It is impossible to know that time has passed unless something changes. In physics, the definition of time is simple- time is change, or the interval over which change occurs. It may be a number on a digital clock, a heartbeat, or the position of the Sun in the sky. Every measurement of time involves measuring a change in some physical quantity. TimeĪs discussed in Physical Quantities and Units, the most fundamental physical quantities are defined by how they are measured. In this section we add definitions of time, velocity, and speed to expand our description of motion. Questions such as, “How long does a foot race take?” and “What was the runner’s speed?” cannot be answered without an understanding of other concepts. There is more to motion than distance and displacement. Figure 2.8 The motion of these racing snails can be described by their speeds and their velocities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
